|
RADIONECROSIS AFTER RADIOTHERAPY IN NASOPHARYNX CANCER
Submitted : 18.03.2024
Accepted : 31.05.2024
Published: 31.05.2024
|
|
Abstract
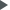
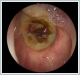
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma is an epithelial neoplasm that originates from the mucosa of the nasopharynx, it is most commonly observed in Rosenmüller fossa. The primary treatment is radiotherapy. Early and late toxicities associated with radiotherapy are present in head and neck cancer. Acute toxicities include mucositis, severe pain, and difficulty swallowing, while late toxicities include xerostomia, trismus, hearing impairment, temporal lobe necrosis, cognitive impairment, cranial nerve injuries, osteoradionecrosis, and carotid artery involvement. Radyonecrosis is one of the most difficult complications to treat after radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. We aimed to evaluate our case who developed deep neck infection with osteoradionecrosis after receiving chemoradiotherapy following nasopharyngeal cancer, in the light of the literature.
|
|
Keywords:
nasopharynx
, nasopharynx carcinoma
, chemoradiotherapy
, radiotherapy
, osteoradionecrosis
, deep neck infection
|
Özet
Nazofarenks karsinomu nazofarenks mukozasından köken alan epitelyal bir neoplazmdır ve en sık Rosenmüller fossada görülür. Temel tedavi radyoterapidir. Baş ve boyun kanserinde radyoterapiye bağlı erken ve geç toksisiteler mevcuttur. Akut toksisiteler arasında mukozit, şiddetli ağrı ve yutma güçlüğü yer alırken, geç toksisiteler arasında kserostomi, trismus, işitme bozukluğu, temporal lob nekrozu, bilişsel bozukluk, kranyal sinir yaralanmaları, osteoradyonekroz ve karotid arter tutulumu yer alır. Radyonekroz, nazofaringeal karsinom için radyoterapi sonrası tedavisi en zor komplikasyonlardan biridir. Nazofarenks kanseri sonrası kemoradyoterapi sonrası osteoradyonekrozlu derin boyun enfeksiyonu gelişen olgumuzu literatür ışığında değerlendirmeyi amaçladık.
|
|
Anahtar kelimeler:
nazofarinks
, nazofarinks karsinomu
, kemoradyoterapi
, radyoterapi
, osteoradyonekroz
, derin boyun enfeksiyonu
|
|
|
|